What is The Difference Between Virtualization and Containerization?
Virtualization & Containerization are advanced technologies that enable the execution of multiple applications or workloads on a single physical machine or host.
Virtual machines & Containers are the two most preferred methods for establishing a software infrastructure for your organization.
Containers have established themselves as a significant component in cloud-native development. Whether used individually or integrated with virtual machines (VMs), they offer countless advantages for your IT system.
Even though they have different capabilities, they share similarities in certain aspects. Both technologies enhance efficiency, provide scalability, introduce flexibility, assist DevOps, & optimize the software development lifecycle.
To boost the efficiency of your IT team and fulfill business needs, you can use containerization and virtualization together.
Difference between Virtualization and Containerization
| Aspect | Virtualization | Containerization |
|---|---|---|
| Isolation | It provides complete isolation from the host operating system and the other VMs | It generally offers lightweight isolation from the host and other containers but doesn’t provide as robust a security boundary as a VM |
| Operating System | Runs a complete operating system, including the kernel, as a consequence, requires more system resources like CPU, memory, and storage | Operates the user-mode portion of an operating system and can be customized to accommodate the needed services for your app using scarce system resources |
| Deployment | Deploy VMs using Hypervisor technology | Deploy containers using Docker or use an orchestrator such as Kubernetes to deploy multiple containers |
| Persistent storage | Uses a Virtual Hard Disk (VHD) for local storage of a single VM & storage shared by multiple servers
Use a Server Message Block (SMB) for file sharing. |
Uses local disks for local storage of a single node & for storage shared by multiple nodes or servers SMB is used |
| Load balancing | In case of a failover cluster virtual machine load balancing is done by running VMs in other servers. | To manage changes in load and availability, an orchestrator automatically starts or stops containers on cluster nodes. |
| Networking | It uses virtual network adapters | Uses an isolated perspective of a virtual network adapter. Thus, it provides less virtualization. |
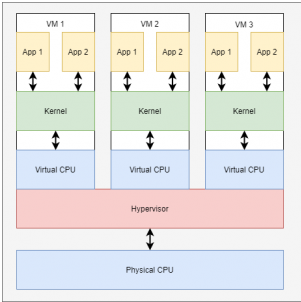
What are virtual machines and virtualization?
Before the emergence of the containers, the “virtual machine” was the preferred choice for optimizing server capacity. Programmed to emulate the hardware and complete operating system of a physical computer, Virtual machines (VMs) and hypervisors enable multiple computers, each with different operating systems on a single physical server’s hardware.
What is a hypervisor?
The hypervisor, also referred to as the virtual machine monitor, is a prerequisite for virtualization. The software or firmware layer allows multiple operating systems to run simultaneously, granting them access to the same physical server resources. The hypervisor effectively partitions and allocates the available computing power, memory, storage, and other resources to each virtual machine as per its requirements.
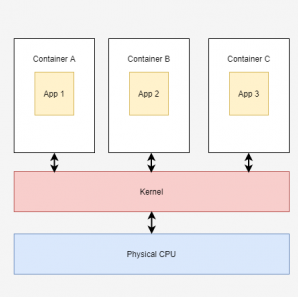
What are containers?
The container uses the host operating system’s kernel, sharing it with other containers, while the shared part of the OS remains read-only. Consequently, the containers are lightweight, enabling the deployment of multiple containers on a single server or a VM.
It quashes the need for dedicating an entire server to a single application, and you only need to manage a single operating system. Scaling up becomes rapid and swift without the need for additional server space.
The container isolates an application from its surroundings by encapsulating its dependencies and configurations within a single unit. After that, the containerized unit can be seamlessly exported to other environments, including private clouds, public clouds, and data centers.
What is containerization?
Containerization is a type of virtualization that imitates your machine's operating system. Containers carry out functions akin to virtual machines but do not encompass hardware virtualization.
Docker is the most extensively used container technology, which uses a public repository. Dependencies like system libraries, external third-party code packages, and other operating system-level programs can be included within a container.
Additionally, an application container allows you to package all the required applications within a portable environment. You can also run multiple containers simultaneously.

Jilesh Patadiya, the visionary Founder and Chief Technology Officer (CTO) behind AccuWeb.Cloud. Founder & CTO at AccuWebHosting.com. He shares his web hosting insights on the AccuWeb.Cloud blog. He mostly writes on the latest web hosting trends, WordPress, storage technologies, and Windows and Linux hosting platforms.